Maintaining a proper tire pressure level is important, if you want to travel safely and smoothly. It affects not only your vehicle’s performance but also your safety on the road. Underinflated tires can lead to reduced traction, decreased fuel efficiency, and increased risk of tire failure. On the other hand, overinflated tires can result in a harsh and uncomfortable ride, decreased braking performance, and uneven tire wear.
In this comprehensive guide, you will learn about the importance of the Tire Pressure Monitoring System, its functionality, and benefits. We’ll also shed light on the different types of TPMS, discuss the TPMS alerts, provide step-by-step instructions on checking and maintaining TPMS, mention the TPMS sensor replacement costs, uncover the TPMS reset and relearn processes, troubleshoot common TPMS issues, and even explore aftermarket TPMS sensors. Get ready!
Table of Contents
What is TPMS?
TPMS stands for Tire Pressure Monitoring System, which is a technology designed to constantly monitor tire pressure and alert the driver if any tire’s pressure falls below the recommended level. By keeping tabs on tire pressure, TPMS helps prevent hazardous situations like tire blowouts, poor handling, and decreased fuel efficiency.
TPMS works by utilizing sensors that are typically installed inside the tires. These sensors measure the tire pressure and transmit the data wirelessly to the car’s onboard computer. When a tire’s pressure deviates from the recommended range, the TPMS system triggers a warning, often indicated by a TPMS light on the dashboard.
Types of TPMS
There are two primary types of TPMS: the indirect TPMS and the direct TPMS. Let’s explore each type to understand how they operate and their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Indirect TPMS
Indirect TPMS relies on the vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) sensors to detect discrepancies in wheel speed. When tire pressure is low, the rolling diameter of the tire decreases, causing it to rotate at a slightly different speed than the other tires. Indirect TPMS compares wheel speed data from the ABS sensors to identify potential pressure loss.
Advantages of Indirect TPMS
- Cost-effective: Indirect TPMS typically uses existing ABS sensors, reducing the need for additional components.
- No sensor replacement: Since it relies on ABS sensors, there are no additional TPMS sensors to replace.
Disadvantages of Indirect TPMS
- Less precise: Indirect TPMS may not provide exact tire pressure readings and can be affected by factors other than tire pressure, such as road conditions and driving habits.
- Limited information: Indirect TPMS may not detect pressure loss in all tires simultaneously, potentially delaying the detection of low tire pressure.
Direct TPMS
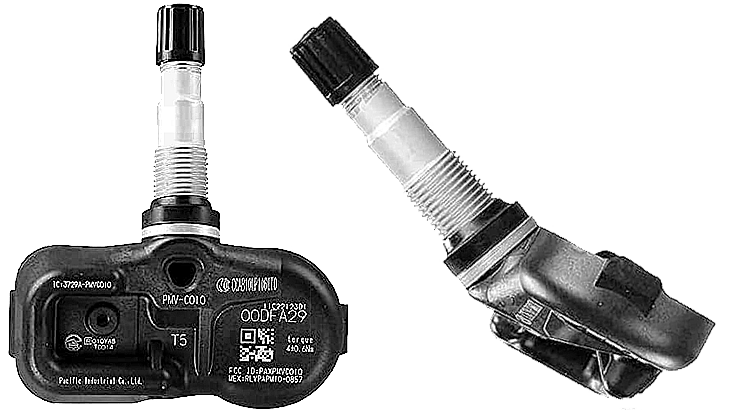
Illustration: Denso 550-0105 Direct TPMS Sensor
Direct TPMS, as the name suggests, directly monitors tire pressure using dedicated pressure sensors installed in each tire. These sensors transmit tire pressure data wirelessly to the central monitoring unit, which then displays the information on your dashboard.
Advantages of Direct TPMS
- Cost-effective: Indirect TPMS typically uses existing ABS sensors, reducing the need for additional components.
- No sensor replacement: Since it relies on ABS sensors, there are no additional TPMS sensors to replace.
Disadvantages of Direct TPMS
- Higher cost: Direct TPMS requires individual sensors for each tire, resulting in higher initial installation costs.
- Sensor replacement: Over time, TPMS sensors may require battery replacement or sensor replacement due to wear and tear.
Understanding the TPMS Alerts
One of the critical aspects of TPMS is understanding the alerts it provides. Let’s check the key components of TPMS alerts and what they mean.
TPMS Sensor
The TPMS sensor is the heart of the system. It continuously measures tire pressure and relays the information to the car’s computer. Each tire is equipped with a sensor, which is often integrated into the valve stem. It’s important to note that TPMS sensor batteries have a limited lifespan and may require replacement.
Common TPMS Alert Symbols and Their Meanings
When your TPMS detects an issue with tire pressure, it will illuminate a warning light on the dashboard. Understanding the symbols associated with these alerts is crucial for taking appropriate action. Common TPMS symbols include an exclamation mark inside a tire, a yellow or red warning light, or a specific tire pressure indicator. Referencing your car’s manual will provide precise details about the symbols and their meanings.

Illustration: TPMS Alert Symbols
What to Do When the TPMS Light Illuminates
When the TPMS light illuminates, it’s essential to address the issue promptly. Start by checking the tire pressure of all four tires using a reliable tire pressure gauge. Inflate or deflate the tires as needed to reach the recommended pressure. If the light persists, it may indicate a problem with the TPMS system itself, requiring professional assistance.
Checking and Maintaining TPMS
To ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of TPMS, regular checks and maintenance are necessary. Follow the steps below to check your tire pressure using TPMS:
Step-by-Step Guide to Checking Tire Pressure Using TPMS
- Start the car and allow the TPMS system to initialize.
- Locate the TPMS display or menu on your dashboard.
- Access the tire pressure readings for each tire.
- Compare the displayed pressure with the recommended pressure for your vehicle.
- If any tire’s pressure is below the recommended range, add air until the desired pressure is reached.
- Double-check the pressure after adding air and adjust as needed.
- Repeat the process for all four tires.
Importance of Regular TPMS Maintenance
Regular TPMS maintenance is crucial for accurate readings and reliable performance. It is recommended to inspect the TPMS sensors during routine tire rotations or service appointments. Clean any dirt or debris around the sensors and ensure they are securely mounted. Additionally, replacing TPMS sensor batteries as needed will prevent signal disruptions and ensure consistent monitoring.
Tips for Maintaining Optimal Tire Pressure
Aside from relying on TPMS, there are other proactive steps you can take to maintain optimal tire pressure:
- Check tire pressure at least once a month and before long trips.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended tire pressure guidelines.
- Inspect tires for any signs of damage, including punctures or bulges.
- Rotate tires regularly to ensure even wear.
- Maintain a safe driving speed and avoid sudden maneuvers that may put stress on the tires.
TPMS Replacement and Sensor Costs
Over time, TPMS sensors may require replacement due to battery depletion or sensor damage. Understanding the process and associated costs can help you make informed decisions.
Overview of TPMS Sensor Replacement and Its Significance
TPMS sensor replacement involves removing the old sensor and installing a new one in its place. It’s essential to replace faulty sensors promptly to ensure accurate monitoring and reliable alerts.
Factors Affecting TPMS Sensor Replacement Cost
Several factors can influence the cost of TPMS sensor replacement, including:
- Vehicle make and model: Sensors for certain vehicles may be more expensive due to their specific requirements.
- OEM vs. aftermarket sensors: Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) sensors are typically pricier than aftermarket options.
- Labor costs: If professional installation is required, labor costs may vary based on the service provider and location.
Tips for Choosing the Right TPMS Sensor
When selecting a TPMS sensor, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the sensor is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Quality: Opt for reliable and reputable brands to ensure accurate readings and longevity.
- Warranty: Check if the sensor comes with a warranty for added peace of mind.
TPMS Reset and Relearn Process
Resetting and relearning TPMS is necessary when replacing tires, sensors, or performing maintenance. Let’s explore the steps involved in this process.
Explanation of TPMS Reset and Relearn Procedures
TPMS reset refers to the process of recalibrating the system to recognize new sensors or tire changes. Relearn, on the other hand, involves teaching the TPMS system the unique identification of each tire’s sensor.
Common Methods for Resetting TPMS
There are several methods for resetting TPMS, including:
- Manual reset: Involves pressing a specific combination of buttons or accessing the TPMS reset button.
- OBD-II reset: Utilizes an onboard diagnostic tool to reset the TPMS system.
- TPMS scan tool reset: Requires a TPMS-specific scan tool for resetting and relearning.
Introduction to TPMS Reset Tools and Their Usage
TPMS reset tools, also known as TPMS relearn tools, are specialized devices designed to reset and relearn TPMS systems. These tools vary in complexity and features, from basic handheld devices to more advanced diagnostic tools. Consult your vehicle’s manual or seek professional advice to determine the most suitable TPMS reset tool for your needs.
Troubleshooting TPMS Issues
While TPMS systems are generally reliable, occasional issues may arise. Understanding common problems and their causes can help you troubleshoot effectively.
Common TPMS Problems and Their Causes
- Sensor battery depletion: Over time, TPMS sensor batteries may deplete, leading to irregular or no signal transmission.
- Sensor damage or corrosion: Physical damage or corrosion can disrupt the sensor’s functionality.
- Signal interference: External factors like electronic devices or nearby transmitters may interfere with TPMS signals.
Troubleshooting Steps for Resolving TPMS Errors
When encountering TPMS errors, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Verify tire pressure manually: Use a reliable tire pressure gauge to confirm the pressure in each tire.
- Check sensor batteries: If TPMS alerts persist, consider replacing sensor batteries as necessary.
- Clean sensors: Remove any dirt or debris around the sensors that may interfere with signal transmission.
- Seek professional assistance: If issues persist or if you’re unsure about troubleshooting steps, consult a qualified technician.
When to Seek Professional Help for TPMS Issues
While basic troubleshooting can resolve many TPMS issues, there are instances when professional help is warranted. Consider seeking professional assistance when:
- TPMS alerts persist despite manual pressure checks and basic troubleshooting.
- Sensor damage or corrosion is evident.
- Advanced diagnostic tools or expertise is required for system reprogramming or repairs.
Aftermarket TPMS Sensors
In addition to OEM sensors, aftermarket TPMS sensors offer an alternative for replacing or upgrading your TPMS system. Let’s explore their benefits and considerations.
What is an aftermarket TPMS Sensor?
Aftermarket TPMS sensors are third-party alternatives to OEM sensors. They offer compatibility with various vehicle makes and models and are often more cost-effective.
Benefits and Considerations of Using Aftermarket TPMS Sensors
- Cost-effectiveness: Aftermarket sensors can be more affordable compared to OEM options.
- Widely available: Aftermarket sensors are readily available from different brands and suppliers.
- Compatibility: Aftermarket sensors offer compatibility with a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
- Quality assurance: Opt for reputable aftermarket brands that provide quality assurance and reliability.
Some Recommended Brands for Aftermarket TPMS Sensors
While there are various aftermarket TPMS sensor brands available, the most popular ones are Schrader, VDO, Huf, and Denso. These brands offer a wide range of compatible sensors for various vehicle makes and models.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
To provide further clarity, let’s address some commonly asked questions regarding TPMS:
As mentioned above, TPMS stands for Tire Pressure Monitoring System.
Yes, run flat tires are compatible with tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS). In fact, TPMS is particularly useful when it comes to run flat tires because it helps monitor the tire pressure and provides early warnings in case of pressure loss.
Manual Reset:
- Start by ensuring all tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Locate the TPMS reset button. It is commonly found in the glove compartment, under the steering wheel, or on the dashboard. Refer to your vehicle’s manual if you’re unsure about the exact location.
- With the engine running, press and hold the TPMS reset button until the TPMS light blinks or illuminates. This may take several seconds.
- Release the button and wait for the TPMS light to turn off. This indicates that the TPMS has been successfully reset.
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) Tool:
- Obtain an OBD tool that is compatible with your vehicle’s TPMS system.
- Ensure all tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Connect the OBD tool to the vehicle’s OBD port, usually located under the dashboard.
- Follow the instructions provided with the OBD tool to initiate the TPMS reset procedure. This may involve navigating through the tool’s menu and selecting the TPMS reset option.
- Wait for the tool to communicate with the vehicle’s TPMS system and perform the reset process. f. Once the TPMS reset is complete, disconnect the OBD tool and verify that the TPMS light has turned off.
The location of the TPMS reset button can vary depending on the vehicle make and model. Here are some common locations where you may find the TPMS reset button:
Glove Compartment: Check the glove compartment of your vehicle. In some models, the TPMS reset button is conveniently located inside the glove compartment.
Under the Steering Wheel: Look underneath the steering wheel column. Some vehicles have the TPMS reset button positioned in this area. It may be on the side or underside of the steering wheel column.
Dashboard: The TPMS reset button could be located on the dashboard, often near the driver’s side. It may be positioned near other controls or indicators, such as the light dimmer switch or hazard button.
Center Console: In certain vehicles, the TPMS reset button can be found on the center console, possibly near the radio or climate control buttons.
Please keep in mind that the TPMS reset button’s specific location can vary even within the same vehicle make and model. It’s always recommended to refer to your vehicle’s manual for the precise location of the TPMS reset button. The manual will provide detailed information and illustrations to help you locate the button accurately.
If you’re unable to locate the TPMS reset button or have difficulty finding it, consulting your vehicle’s manual or contacting a dealership or authorized service center for assistance is advised.
Disabling the TPMS entirely can compromise your safety and may even be illegal in some jurisdictions. However, there are situations where temporarily disabling the TPMS may be necessary, such as when using snow chains or installing aftermarket wheels that do not have TPMS sensors.
To temporarily disable the TPMS, the most common pattern is to inflate the tires to the recommended pressure while the vehicle is stationary, then start the engine and drive the vehicle for a short distance. This will trigger the TPMS to perform a self-check and may result in a temporary TPMS warning light illumination. Once the TPMS warning light is on, it should remain steady or flash for a specific period, indicating that the TPMS is temporarily disabled. However, it’s important to note that this procedure may vary depending on the vehicle make and model, and it’s always recommended to consult your vehicle’s manual for the specific instructions related to TPMS disabling.
It’s crucial to remember that the TPMS is a safety feature designed to monitor tire pressure and ensure optimal driving conditions. Disabling or tampering with the TPMS without a legitimate reason can increase the risk of tire-related accidents and may void your vehicle’s warranty. If you have concerns or need to disable the TPMS for a specific reason, it’s best to consult with a professional technician or your vehicle manufacturer for guidance and assistance.
Testing the TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System) sensor battery can be challenging as the sensor’s battery is typically sealed and not designed for individual replacement. However, there are a few methods you can try to assess the battery status:
TPMS Warning Light: If the TPMS warning light illuminates on your vehicle’s dashboard, it may indicate a low battery in one or more TPMS sensors. Keep in mind that the warning light can also be triggered by other factors, such as low tire pressure or a faulty sensor.
Professional Diagnostic Tool: A professional technician with specialized TPMS diagnostic equipment can perform a battery voltage test on each sensor. This diagnostic tool can communicate with the TPMS sensors and provide information about battery voltage levels.
Sensor Replacement: If you suspect a dead or low battery in a TPMS sensor, one way to test it is by replacing the sensor with a new one. If the TPMS warning light goes off after the replacement, it suggests that the original sensor’s battery was indeed dead or low.
Regularly checking tire pressure is essential for safe driving. But generally speaking, tire pressure should be checked at least once every month and before you go on long trips.
Replacing TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System) sensors yourself is possible, but it can be a more complex task compared to basic maintenance procedures. Here is a general guide on how to replace TPMS sensors:
Determine the Faulty Sensor: If you have a TPMS warning light indicating a faulty sensor, identify which specific sensor requires replacement. Some TPMS systems provide information on the specific tire position, while others may require additional diagnostics to pinpoint the faulty sensor.
Obtain the Correct Sensor: Contact your vehicle manufacturer, authorized dealership, or a reputable auto parts store to purchase a TPMS sensor that is compatible with your vehicle make and model. Ensure the new sensor matches the specifications of the original sensor, including frequency and sensor type.
Gather the Necessary Tools: Depending on your vehicle and the sensor replacement method, you may need tools such as a jack, lug wrench, torque wrench, valve stem tool, and TPMS programming tool (if required).
Lift the Vehicle: Use a jack to lift the vehicle off the ground, following proper safety procedures and referring to your vehicle’s manual for specific jacking points.
Remove the Wheel: Use a lug wrench to loosen and remove the lug nuts, then carefully remove the wheel from the vehicle.
Locate the Sensor: Find the TPMS sensor, which is attached to the valve stem inside the wheel. It may be necessary to remove the tire from the rim to access the sensor.
Remove the Old Sensor: Depending on the sensor design, you may need to unscrew the sensor or release it using a specific tool. Be cautious not to damage the valve stem or the wheel during the removal process.
Install the New Sensor: Insert the new TPMS sensor into the valve stem hole, ensuring it is properly aligned. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for tightening the sensor to the recommended torque.
Reassemble the Wheel: Remount the tire onto the wheel rim, taking care to align the tire’s balance marks with the valve stem. Tighten the lug nuts by hand until they are snug.
Lower the Vehicle and Torque the Lug Nuts: Carefully lower the vehicle to the ground using the jack. Use a torque wrench to tighten the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specifications in a star or cross pattern.
Repeat for Other Sensors: If you are replacing multiple sensors, repeat steps 4 to 10 for each wheel.
Reset the TPMS: After replacing the sensors, you may need to perform a TPMS reset or relearn procedure to ensure the system recognizes the new sensors. Refer to your vehicle’s manual for specific instructions on how to reset the TPMS.
It’s important to note that some vehicles require the TPMS sensors to be programmed or synced to the vehicle’s TPMS system using a programming tool or by visiting a dealership or professional service center. If you’re uncertain about the process or lack the necessary tools and expertise, it’s recommended to consult a professional technician who can safely and accurately replace the TPMS sensors for you.
The cost of TPMS sensor replacement can vary depending on factors such as the vehicle make and model, the type of sensors required, and labor costs. It is best to consult with automotive professionals or service centers for accurate cost estimates. But typically the prices range from $50 to $200 per sensor, including installation.
When the TPMS light is illuminated, it indicates a potential issue with tire pressure or the sensor. It’s important to check the tire pressure manually and take appropriate action based on the readings.
Yes, aftermarket TPMS sensors are available as alternatives to OEM sensors. They offer compatibility with various vehicles and can provide cost-effective solutions. As described above, the most popular ones are Schrader, VDO, Huf, and Denso.
We hope these answers have shed light on some common questions related to tire pressure monitoring system. If you have any further inquiries or need personalized assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out to a tire professional or refer to your vehicle’s manufacturer guidelines.
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) play a vital role in ensuring road safety by constantly monitoring tire pressure and alerting drivers to any deviations from the recommended range. By understanding the importance of TPMS, the types of systems available, how to interpret TPMS alerts, and the maintenance and troubleshooting aspects, you can proactively safeguard yourself and your passengers while enjoying a smooth and worry-free driving experience.
Remember to regularly check your tire pressure, perform routine TPMS maintenance, and address any issues promptly. Whether you opt for OEM or aftermarket TPMS sensors, prioritize quality and compatibility. By following these guidelines and arming yourself with knowledge, you can confidently navigate the roads, knowing that you have a reliable TPMS system keeping you safe.
Safe travels and happy driving!